3D Printing
3D printing is a production technology in which three-dimensional objects are built layer by layer. This technology digital models created using computer-aided design (CAD) software to physical objects used to transform. 3D printing is also known as “additive manufacturing” or “rapid prototyping”. Here are the main features of 3D printing:
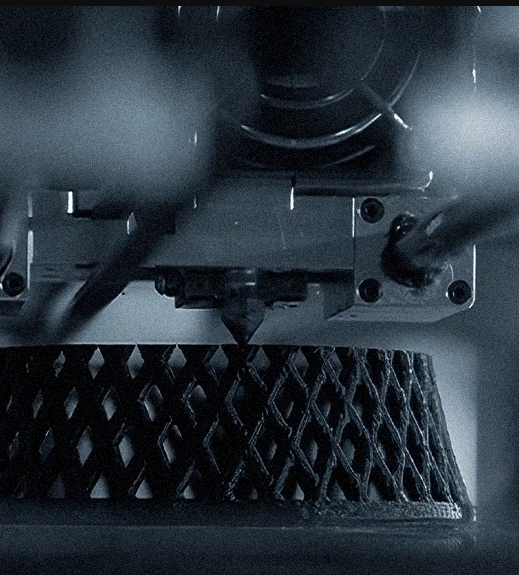
Working Principle:
3D printing allows material to be assembled in layers to create an object. These layers are created with information from a digital design file.
Materials:
The materials used in 3D printing have a wide range. Different materials such as plastic, metal, ceramic, resin and even biological materials can be used. The choice of material depends on the intended use and design requirements of the object.
Application Areas:
3D printing is used in prototype development, manufacturing, medical, education, construction, fashion and a range of other industrial sectors. It is particularly popular for the rapid production and prototyping of custom and complex parts, as well as the production of personalised products.
Rapid Prototyping:
3D printing allows designs to be quickly converted into physical prototypes. This can speed up the product development process and reduce costs.
Sustainability:
3D printing has the potential to minimise material waste. Unlike traditional production methods, it allows only the necessary material to be used.
3D printing technology is constantly evolving and is being widely adopted across industries. The use of this technology has the potential to optimise and speed up production processes and make them more sustainable. has the potential to bring.